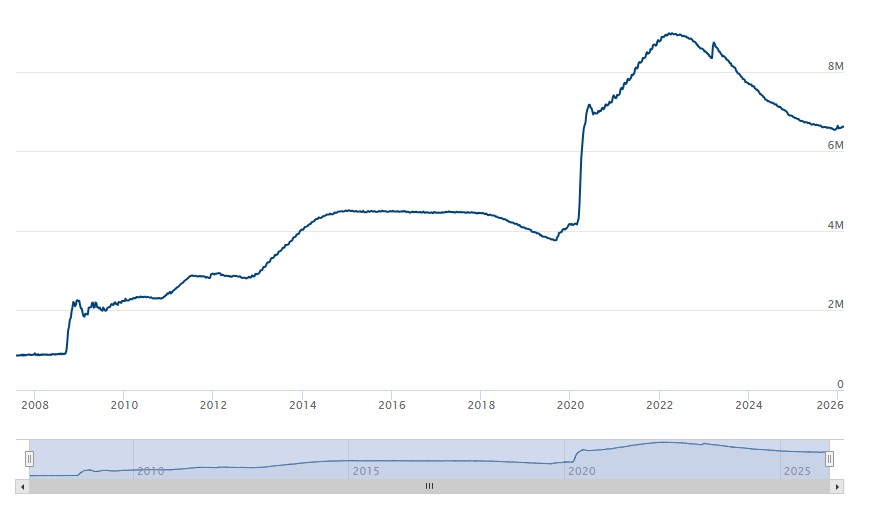
ALT-Coins
Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum is a decentralized platform for decentralized applications (DApps) based on smart contracts. In addition to the cryptocurrency Ether (ETH), it also enables the creation and management of tokens, decentralized finance (DeFi), games, and digital collectibles (NFTs). Use cases range from initial coin offerings (ICOs) and prediction markets to applications in the field of rights management and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Basic functions and applications
Smart Contracts
Ethereum enables the execution of automated contracts (smart contracts), which are self-executing agreements whose terms are written directly into code.
DApps (Decentralized Applications)
These smart contracts form the basis for decentralized applications that are not controlled by a central authority, as is the case with traditional apps.
Areas of application for Ethereum
Decentralized finance (DeFi)
This is one of the largest use cases, where users can access financial services such as lending, trading, and insurance in a decentralized manner.
Digital assets and tokens
Ethereum is used to create various tokens, including:
- ERC-20 tokens: Fungible tokens for various purposes, similar to digital currencies.
- ERC-721 tokens (non-fungible tokens, NFTs): Non-fungible tokens that represent unique digital collectibles or assets.
Own cryptocurrency (Ether, ETH)
ETH is the native currency of the network and is required to conduct transactions and pay gas fees for the execution of smart contracts.
DApps (Decentralized Applications)
Developers can create a variety of DApps on Ethereum that can serve different purposes.
supply chain management
The network enables the tracking and authentication of products in a supply chain, which increases transparency.
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs)
Ethereum serves as the basis for DAOs, which enable decentralized decision-making.
Games and gambling:
The platform is also used for decentralized games and gambling applications.
Crowdfunding (ICOs)
Projects can raise capital through Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) by issuing new tokens.
Rights Management
Artists and creators can manage their works directly via Ethereum and receive royalties via smart contracts, eliminating the need for middlemen such as collecting societies.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Ethereum can serve as the basis for the global networking of IoT devices and provide a common, fault-resistant communication interface.
The role of Ether (ETH)
Network costs (gas)
Ether is Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency and is referred to as “gas” to pay for transactions and the execution of smart contracts on the network.
Store of value and means of payment
ETH can also be used as a store of value or means of payment, similar to Bitcoin.
Staking
Users can stake ETH to secure the network and receive rewards in return.
Chainlink (LINK)
Chainlink (LINK) is a decentralized oracle network that connects smart contracts with real-world data, such as cryptocurrency prices, weather data, or sports scores, enabling them to operate reliably and transparently in the real world. The LINK token is used to pay Chainlink node operators for providing and validating this data, to enable staking to secure the network, and to participate in governance.
Main application: Bridge between blockchains and the real world
Solving the Oracle Problem
Chainlink bridges the gap between isolated smart contracts on the blockchain and external, off-chain data sources.
Data access for smart contracts
Smart contracts can obtain secure access to a wide range of data via Chainlink, e.g.:
- Prices of cryptocurrencies or other assets
- Results of sporting events
- Weather information
- Data from APIs and databases
Enables real-world applications
Access to this data enables smart contracts to be used in the real world, for example in areas such as insurance, prediction markets, or decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
Using the LINK token
Payment for oracle services
Node operators who retrieve and deliver data are paid with LINK tokens to compensate them for their work.
Staking
Token holders can “stake” their LINK tokens to contribute to the security and integrity of the Chainlink network.
Incentives for data providers
The token incentivizes node operators to provide accurate and timely data, which increases the reliability of data for smart contracts.
Governance
In some Chainlink-based projects, the LINK token is also used for governance purposes, allowing token holders to vote on the direction of the project.
Ripple (XRP)
The primary use of XRP, Ripple’s cryptocurrency, is as a bridge currency for fast, low-cost cross-border payments within the Ripple network for financial institutions such as banks and payment service providers. XRP is also used to pay transaction fees on the XRP Ledger, with the fees being burned to secure the network and prevent spam. In addition, XRP is used in the digitization of assets, for example by central banks for digital currencies (CBDCs) or the tokenization of real estate.
Main areas of application
Bridge currency for international payments
XRP acts as an intermediary in currency conversions to make transactions between different fiat currencies faster and more cost-effective.
Transaction fees
Every transaction in the XRP Ledger requires a small fee, which is paid in XRP and then burned, contributing to security and preventing spam.
Infrastructure for financial service providers
Ripple Net uses XRP for its products and services, which are tailored to the needs of banks and other financial companies.
Digital assets and CBDCs
There are use cases where XRP is used for the issuance and transfer of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) or other digital assets such as real estate tokens.
Key features
Energy efficiency
Unlike energy-intensive cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, XRP uses an efficient consensus mechanism that requires less energy.
Velocity
The XRP Ledger enables very fast transaction settlements in just a few seconds.
Low costs
Transaction fees are extremely low, making it attractive for global payment flows.
SUI
The native SUI token is used in the Sui network for transaction fees, staking to secure the network and rewards, participation in governance, and as the native currency for various decentralized applications (DeFi) and games (GameFi). Its application is versatile and aims to secure the network, enable decentralized decision-making, and support a wide range of applications through the Move programming language and a scalable architecture.
Applications of the SUI token:
Payment of gas fees
Users utilize SUI tokens to pay the fees for conducting transactions and executing smart contracts on the Sui network.
Staking
By staking SUI tokens, holders can contribute to the security of the network and receive staking rewards in return.
Governance
SUI token holders have the opportunity to participate in the future governance of the network and make decisions about its further development.
Native currency
The SUI token serves as the basic means of payment for various applications built on the Sui blockchain, including decentralized financial services (DeFi) and gaming (GameFi).
What the Sui blockchain is used for:
Secure smart contracts
SUI uses the Move programming language, which aims to make smart contracts more secure and efficient and minimize vulnerabilities such as reentrancy attacks.
Decentralized applications (dApps)
The platform is ideal for developing and operating dApps in areas such as DeFi and GameFi.
NFT applications
Sui’s fast transaction processing is particularly advantageous for the creation, trading, and further development of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), especially in the gaming sector.
Simplified access
With ZkLogin, SUI offers a unique feature that allows users to log in with existing Web2 accounts, thereby lowering the barrier to entry for Web3.
Scalability
SUI’s architecture enables high scalability, both in transaction processing and data storage, which is cost-effective for many applications.
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot is a multi-chain blockchain platform whose main application is to connect different blockchains to enable secure data exchange and interoperability. By creating a network of specialized blockchains and a central main chain, Polkadot aims to improve the scalability and security of blockchains and support a decentralized internet.
Main applications and objectives
Interoperability
Polkadot enables different, independent blockchains to seamlessly exchange information and value, solving the problem of isolation.
Scalability
The system is designed to be highly scalable by using specialized blockchains (parachains) that process data and transactions in parallel.
Aggregate security
All blockchains connected to the network can access the security of the central relay chain network.
Decentralized Internet (Web3)
Polkadot provides the infrastructure for a new generation of the internet, where users have control over their data.
Platform for decentralized applications (dApps)
It simplifies the creation and operation of decentralized applications, institutions, and services that can operate on different chains.
How it works
Relay chain
The central main chain is responsible for security and communication between the parachains.
Parachains
These are specialized blockchains that are connected to the relay chain and can be optimized for specific use cases.
DOT tokens
The platform’s native token serves various purposes, including staking to secure the network, voting on governance, and connecting parachains.
Cardano (ADA)
Cardano is a blockchain platform and cryptocurrency that aims to create a secure and scalable infrastructure for decentralized applications (dApps), similar to Ethereum, but with a stronger focus on scientific research and an energy-efficient proof-of-stake consensus mechanism called Ouroboros. The platform’s native cryptocurrency is ADA, which is used for transaction fees and to participate in network consensus.
Key features of Cardano
Scientific approach
Cardano emphasizes thorough research and peer review processes to ensure a secure and stable platform.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Unlike Bitcoin, which uses proof-of-work, Cardano uses a more energy-efficient PoS mechanism (Ouroboros) to validate transactions and generate new coins.
Scalability
The platform is designed to solve scaling issues faced by other blockchains and offer the ability to process a large number of transactions.
Decentralized applications (dApps)
Developers can create their own decentralized applications and smart contracts on Cardano.
Multi-layer architecture
Cardano uses a two-layer structure (settlement layer and computation layer), which enables better security, flexibility, and scalability.
Token standard
Cardano enables the creation of “native” tokens, which, like the ADA coins themselves, are first-class citizens on the blockchain, leading to greater security and lower transaction costs.
The ADA cryptocurrency
purpose
ADA is the native token of the Cardano blockchain and is used to pay transaction fees, participate in the proof-of-stake mechanism (staking), and for other network services.
Security
ADA is the native token of the Cardano blockchain and is used to pay transaction fees, participate in the proof-of-stake mechanism (staking), and for other network services.
Solana (SOL)
The Solana cryptocurrency (SOL) is primarily used as a means of payment for transactions and smart contracts within the Solana network, serves to secure the network through staking, and enables the development of decentralized applications (dApps) such as DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces, blockchain games, and payment systems. Thanks to its high speed and low fees, Solana is particularly well suited for applications that require high transaction capacity.
Areas of application for Solana (SOL)
Decentralized finance applications (DeFi)
Solana enables the creation and use of DeFi platforms such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending protocols, and liquidity platforms that allow for fast and low-cost transactions.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
NFTs can be created, traded, and managed on the Solana blockchain. Platforms such as Magic Eden leverage Solana’s advantages for NFT marketplaces.
Blockchain gaming and the metaverse
The high transaction speed makes Solana an ideal platform for blockchain games, where in-game assets are managed and the gaming experience is optimized.
Payment systems
Solana enables fast and low-cost micropayments and international transactions. Solana Pay allows merchants to accept and make direct crypto payments.
Development of dApps
Solana is a powerful platform for developing and executing smart contracts, enabling the creation of a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps).
How is SOL used?
transaction fees
Users pay SOL to execute transactions and smart contracts on the Solana blockchain.
Staking
SOL can be staked to secure the network and receive rewards in return.
Access to the Solana ecosystem
The SOL token provides access to the various services and functions offered within the Solana ecosystem.