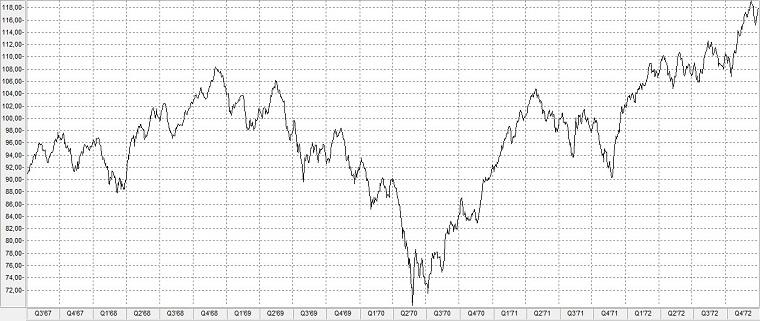
In the so-called, almost forgotten, tech crash of 1970, the S&P 500 Index fell a total of 36.1% from its high of 108.37 points reached on 29 November 1968 to a low of 69.29 points by 26 May.
Development of the S&P 500 from July 1967 to December 1972
Progression of the crisis
S&P 500 Höchststand bei 108,37 Punkten.
S&P 500 Tiefststand bei 69,29 Punkten.
Vollständige Erholung des S&P 500.
Causes
A period of excessive euphoria, preceding most crashes and in this case spurred by the first moon flights of the Apollo missions, sent share prices soaring to extreme heights.
However, despite the boom in the technology and computer industries, there was an extreme crash in share prices. The main cause of the crash, just like the bursting of the dotcom bubble in 2000, was low or no corporate profits. The average price-earnings ratio of technology stocks in 1968 was 114. Computer manufacturers were trading at 103 times their earnings. By comparison, stocks in the Dow Jones Index had an average P/E ratio of 16 in the peak year of 1968.
IBM, for example, could not meet the growing demand for its new System 370. The distribution system of bundling hardware and software was questioned by the Department of Justice and resulted in a 13-year-old lawsuit, the substance of which was eventually overtaken by developments in the industry and eventually shelved.
7 Medium-term fractal indicators - 1969

7 Medium-term fractal indicators - 1970