This post-WWII bear market was caused by investors mistakenly assuming that the end of wartime spending would result in an economic slowdown. Instead, there was a period of massive inflation and pent-up demand as those returning from the war tried to regain their footing.
The pent-up demand after World War 2 led to an increase in inflation and speculation. As a result, in January 1946, regulators increased margin requirements for stock purchases from 75% to 100%. To meet these new requirements, many investors had to sell their shares, which contributed to the market going into a tailspin.
History
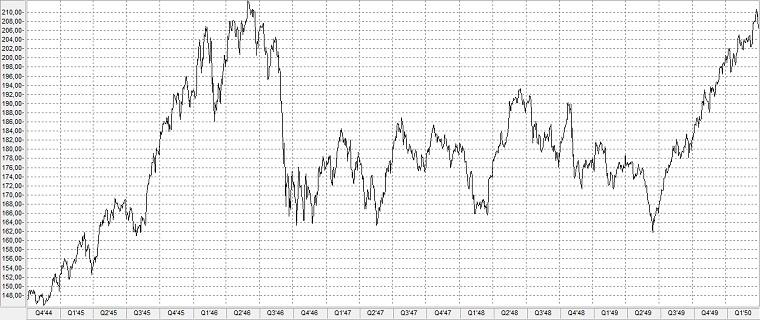
During the stock market crash, the Dow Jones Industrial Average lost 23.2% of its value in just over four months immediately after the Second World War. The Dow Jones peaked on 29 May 1946 at 212.50 points before bottoming out at 163.12 points on 9 October 1946.
Development of the DIJA from October 1944 to March 1950
Progression of the crisis
Der Dow Jones Index erreicht seinen Höchststand von 212,50 Punkten,
Der DIJA liegt bei 195 Puntken.
Der Dow Jones Index erreicht 161,60 Punkte und markiert damit das Ende des Bärenmarktes.
7 Medium-term fractal indicators - 1945
7 Medium-term fractal indicators - 1946